EV Charging 101: Your Guide to Electric Vehicle Infrastructure
We've built our expertise on delivering reliable, uptime-focused charging solutions for commercial and industrial applications. This guide provides comprehensive information, from the basics of charging levels for new drivers to the advanced protocols and load management techniques critical for seasoned professionals and infrastructure investors.
Types of Electric vehicles
Hybrid Electric Vehicle
(HEV)
An HEV combines an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor. These vehicles may be able to run on battery only on a very limited range
or supplement power to the ICE engine.
Battery is charged by the ICE engine or by regenerative braking.
Does not have a charging port. Therefore is unable to charge at a charging station.
Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
Similar to an HEV, in that it has both a battery and an ICE. These vehicles typically have a little larger battery for additional electric range.
A PHEV is a hybrid electric vehicle that has a battery that can be recharged by being plugged in, as well as a combustion engine.
Typically these vehicles can only be charges with an AC Level 2 charging station.
Battery Electric Vehicle
(BEV)
A BEV is a fully electric vehicle (no ICE).
The greatest potential for environmental and operating cost savings.
Battery ranges can vary from 100 to 400+ miles.
The majority of BEV’s can charge with both slower level 2 chargers and DC fast chargers.
DC fast charging power is dependent upon vehicle capability, the charging station power (and/or amps), or even occasionally; utility demand requests and responses or network load management settings, that manage power from the grid to provide capacity to other infrastructure and/or to keep costs down to the network and EV driver.
Heavy-Duty
These Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) are fundamental to maximizing OpEx reduction and achieving zero-emission port and logistics mandates.
High-capacity Lithium-Ion battery packs, often 720 VDC, demand specialized DC Fast Charging (CCS1 up to 360 kW) to support continuous, multi-shift operations. The future will mandate Megawatt Charging System (MCS) readiness.
Effective deployment requires EV Range’s Intelligent Load Management Software. This system minimizes crippling utility demand charges and optimizes the complex power distribution required for entire industrial fleets.
Types of EV Charging Stations
Level 1 (AC)
Typical Location
Home (Standard 120V Outlet)
Voltage
120V Single Phase AC
Amps
12-16 Amps
Typical Power Output
1kW - 1.9kW
Charging Time
3-5 Miles of Range Per Hour
Uses a standard 120-volt household outlet. It’s convenient for residential overnight charging but is too slow for commercial applications.
Level 2 (Ac)
Typical Location
Home, Workplace, Retail, Hospitality
Voltage
208V- 240V Single Phase AC
Amps
12-80 Amps
Typical Power Output
3kW - 22kW
Charging Time
10-75 Miles of Range Per Hour
Operates on 208-volt (commercial) or 240-volt (residential) power. This is the most common charging type for destinations where vehicles park for several hours, like workplaces and hotels, due to its reliability and consistent uptime.
Level 3 (DC Fast Charging)
Typical Location
Highway Corridors, Fleet Depots, High-Traffic Public Sites, Shipping Ports, Mines, Agriculture
Voltage
480V Single Phase
Amps
100 - 600 Amps
Typical Power Output
30kW - 360kW
Charging Time
180 - 240 Miles of Range Per Hour
This method bypasses the car's onboard converter and delivers high-power Direct Current (DC) directly to the battery. It is ideal for fleet operations and public sites requiring rapid turnaround. DCFC typically requires a 480V three-phase electrical service.
Types of Connectors
J1772
(Level 1 and 2)
This connector is capable of AC Level 1 and AC Level 2 charging only.
CHAdeMO
(DC Fast Charging - Level 3)
A standard connector for DC fast charging developed in Japan. Many Asian automakers have released vehicles in North America that use CHAdeMO, although recently some have begun to switch to the higher-power CCS. Tesla offers a CHAdeMO adaptor for their cars, making it possible for Tesla vehicles to charge at public DCFC stations with CHAdeMO.
CCS
(DC Fast Charging - Level 3 & 4)
Combined Charging System (CCS) is an upgraded fast charge version of the J1772 which is used by most US and European automakers. Level 4 charging is made possible by liquid cooling the cable to reduce weight.
NACS
(DC Fast Charging - Level 3 & 4)
Until recently, Tesla's connector has exclusively been available for only Tesla vehicles only, since the connector was proprietary to Tesla. That is until the announcement of opening the connector to others and renaming the connector to NACS.
EV Range shall be providing NACS connectors on stations in the near future given the announcement of numerous automakers.
Solar & Battery Energy Storage
Solar Photovoltaic Systems
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) systems generate clean energy that can power charging stations, significantly reducing long-term electricity costs and supporting sustainability mandates.
Financial Benefit: Using solar energy directly reduces reliance on utility power, decreasing operational expenses.
Green Charging: Allows for certified "green charging" initiatives, which is a major factor for corporate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting.
Utility Rate Mitigation: Helps to offset expensive Time-of-Use (TOU) rates by supplying power during peak demand periods.
Battery Energy Storage Systems
BESS, or large-scale batteries, are essential components for maximizing financial return and stabilizing the grid impact of high-power DC Fast Charging (DCFC) deployments.
Demand Charge Mitigation: This is the most critical B2B function. BESS stores inexpensive off-peak electricity and discharges it during peak periods, directly shaving the most expensive power demand peaks that trigger crippling utility demand charges.
Grid Resilience: Provides essential backup power, ensuring charging station uptime even during grid disruptions, which is crucial for fleet operations.
Optimizing Renewable Energy: BESS allows for storing excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during peak charging windows.
Revenue Generation: Enables participation in utility demand response programs, allowing the BESS to act as a distributed energy resource (DER) and generate revenue for the site owner.
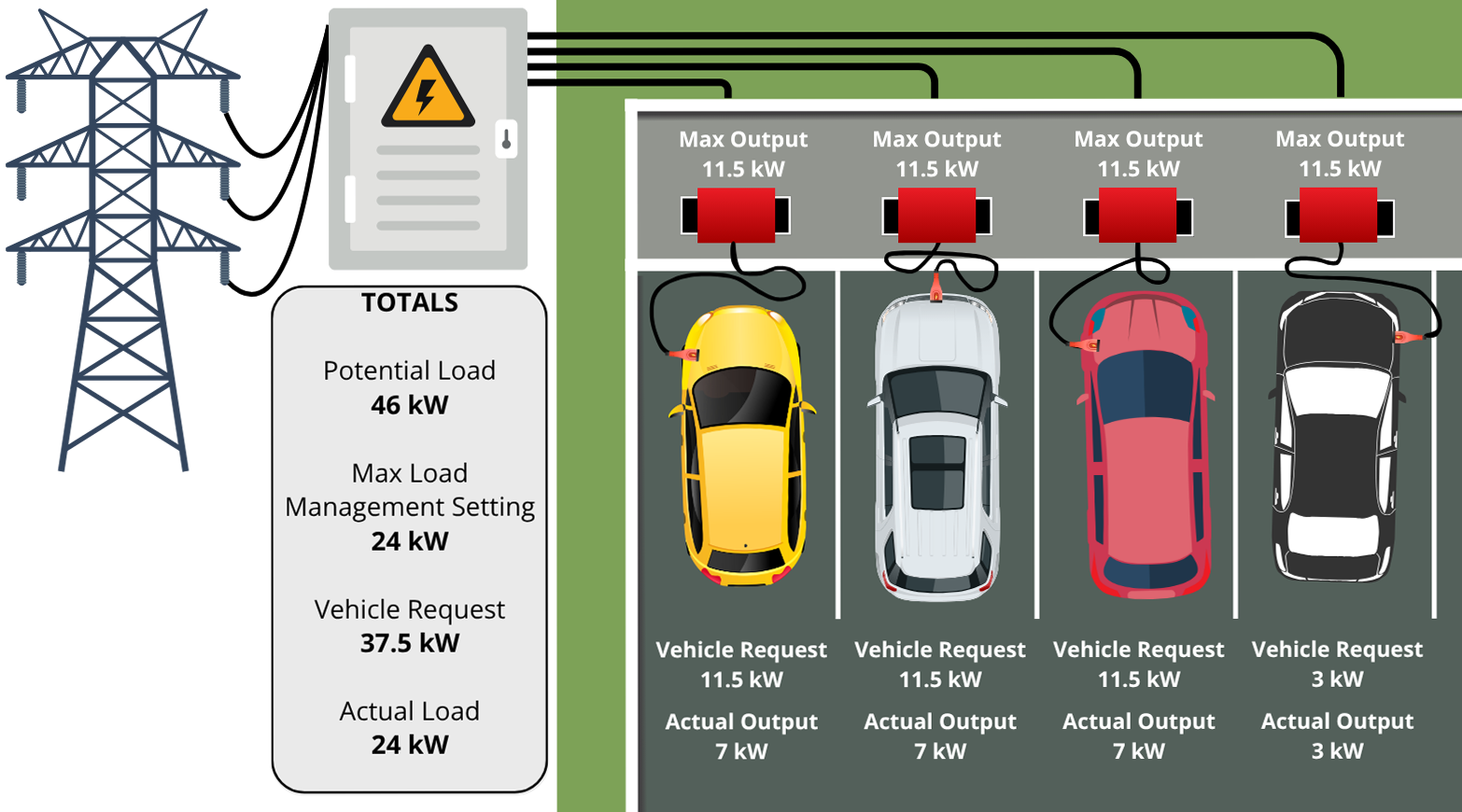
Intelligent Load Management
For any commercial site with multiple chargers, the primary challenge is managing high electrical demand without triggering expensive demand charges or requiring prohibitively costly utility upgrades. Load management systems solve this by balancing the power draw across all site loads.
EV Range's Dynamic Load Management: Our DLM systems deliver demand charge mitigation and optimize charging based on factors like current grid capacity and building demand. This allows you to install more chargers on existing infrastructure and maximize your system's capacity.
Advanced Standards and Interoperability
The global EV ecosystem relies on a common digital "language" to ensure a charger from one vendor can communicate with a network management system from another. EV Range ensures hardware-agnostic compatibility through strict adherence to these protocols.
OCPP Compliance
OCPP Compliance (Open Charge Point Protocol):
The Foundation of Interoperability: OCPP enables seamless communication between charging stations (hardware) and the central management system (software). This prevents vendor lock-in and allows operators to mix and match equipment.
EV Range uses OCPP 1.6J to guarantee future scalability and security.
ISO 15118
ISO 15118 (Plug & Charge):
This standard defines vehicle-to-grid communication, allowing the car and charger to automatically authenticate and handle billing without the need for RFID cards or mobile apps. It uses secure certificate-based communication (PKI) and is V2G ready.
CTEP/NTEP
CTEP/NTEP Certification (Regulatory Compliance):
Especially critical in California (CTEP), these certifications establish measurement standards for commercial charging equipment to ensure accurate energy measurement and transparent kilowatt-hour pricing for the customer. EV Range maintains full CTEP compliance across our hardware portfolio.